目录
1.介绍
YOLOv5%E3%80%81YOLOv8%E6%94%B9%E8%BF%9B-toc" style="margin-left:0px;">2. YOLOv5、YOLOv8改进
2.1 common.py配置
2.2 yolo.py配置
2.3 yaml配置文件
1.介绍
视觉领域正在见证从 CNN 到 Transformers 的建模转变,纯 Transformer 架构在主要视频识别基准测试中达到了最高准确度。这些视频模型都建立在 Transformer 层之上,Transformer 层在空间和时间维度上全局连接块。在本文中,我们提倡视频 Transformer 中的局部归纳偏差,与以前的方法相比,即使使用时空分解,也可以在全局范围内计算自注意力,从而实现更好的速度-精度权衡。所提出的视频架构的局部性是通过调整为图像域设计的 Swin Transformer 实现的,同时继续利用预训练图像模型的力量。我们的方法在广泛的视频识别基准测试中实现了最先进的准确度,包括动作识别(Kinetics-400 上的 84.9 top-1 准确度和 Kinetics-600 上的 85.9 top-1 准确度,减少了约 20× 预训练数据和小模型尺寸的 3 倍)和时间建模(SomethingSomething v2 上的 69.6 top-1 准确率)。
论文地址Swin-Transformer论文下载论文地址
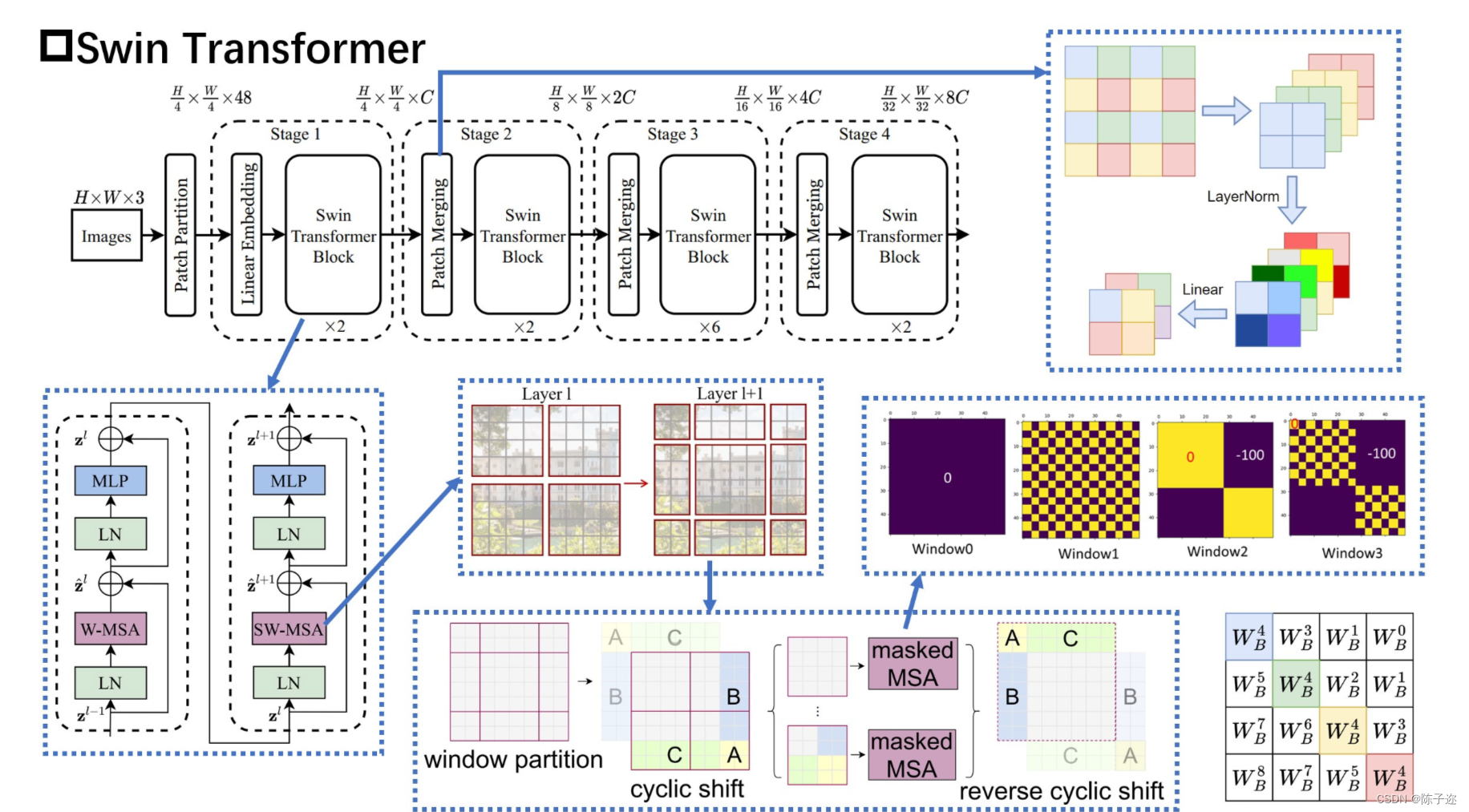
该论文介绍了一种名为 Swin Transformer 的新视觉 Transformer,它能够作为计算机视觉的通用主干。将 Transformer 从语言适应到视觉的挑战来自两个领域之间的差异,例如视觉实体的规模变化很大,以及与文本中的单词相比,图像中像素的高分辨率。为了解决这些差异,我们提出了一种分层 Transformer,其表示是用移位窗口计算的。移位窗口方案通过将 self-attention 计算限制在不重叠的本地窗口上,同时还允许跨窗口连接,从而带来更高的效率。这种分层架构具有在各种尺度上建模的灵活性,并且具有相对于图像大小的线性计算复杂度。Swin Transformer 的这些特性使其与广泛的视觉任务兼容,包括图像分类(ImageNet-1K 上 86.4 top-1 准确度)和密集预测任务,例如对象检测(COCO 测试上 58.7 box AP 和 51.1 mask AP dev)和语义分割(ADE20K val 为 53.5 mIoU)。它的性能大大超过了之前的 state-of-the-art,在 COCO 上 +2.7 box AP 和 +2.6 mask AP,在 ADE20K 上 +3.2 mIoU,展示了基于 Transformer 的模型作为视觉骨干的潜力。代码和模型将在 它的性能大大超过了之前的 state-of-the-art,在 COCO 上 +2.7 box AP 和 +2.6 mask AP,在 ADE20K 上 +3.2 mIoU,展示了基于 Transformer 的模型作为视觉骨干的潜力。代码和模型将在 它的性能大大超过了之前的 state-of-the-art,在 COCO 上 +2.7 box AP 和 +2.6 mask AP,在 ADE20K 上 +3.2 mIoU,展示了基于 Transformer 的模型作为视觉骨干的潜力。
面临问题:
作者提出了将Swin Transformer缩放到30亿个参数的技术 ,并使其能够使用高达1536×1536分辨率的图像进行训练。在很多方面达到了SOTA。
目前,视觉模型尚未像NLP语言模型那样被广泛探索,部分原因是训练和应用中的以下差异:
(1)视觉模型通常在规模上面临不稳定性问题;
(2)许多下游视觉任务需要高分辨率图像,如何有效地将低分辨率预训练的模型转换为高分辨率模型尚未被有效探索,也就是跨窗口分辨率迁移模型时性能下降。
(3)当图像分辨率较高时,GPU显存消耗也是一个问题。
解决思路:
为了解决这些问题,作者提出了几种技术,并在本文中以Swin Transformer进行了说明:
(1)提高大视觉模型稳定性的后归一化(post normalization) 技术和缩放余弦注意力(scaled cosine attention)方法,以提高大型视觉模型的稳定性;
(2)一种对数间隔连续位置偏差技术(log-spaced continuous position bias technique) ,用于有效地将在低分辨率图像中预训练的模型转换为其高分辨率对应模型。
(3)分享节约GPU内存消耗方法,使得训练大分辨率模型可行;
YOLOv5%E3%80%81YOLOv8%E6%94%B9%E8%BF%9B">
2. YOLOv5、YOLOv8改进
2.1 common.py配置
在./models/common.py文件中增加以下模块,直接复制即可
class SwinTransformerBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, c1, c2, num_heads, num_layers, window_size=8):
super().__init__()
self.conv = None
if c1 != c2:
self.conv = Conv(c1, c2)
# remove input_resolution
self.blocks = nn.Sequential(*[SwinTransformerLayer(dim=c2, num_heads=num_heads, window_size=window_size,
shift_size=0 if (i % 2 == 0) else window_size // 2) for i in range(num_layers)])
def forward(self, x):
if self.conv is not None:
x = self.conv(x)
x = self.blocks(x)
return x
class WindowAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, window_size, num_heads, qkv_bias=True, qk_scale=None, attn_drop=0., proj_drop=0.):
super().__init__()
self.dim = dim
self.window_size = window_size # Wh, Ww
self.num_heads = num_heads
head_dim = dim // num_heads
self.scale = qk_scale or head_dim ** -0.5
# define a parameter table of relative position bias
self.relative_position_bias_table = nn.Parameter(
torch.zeros((2 * window_size[0] - 1) * (2 * window_size[1] - 1), num_heads)) # 2*Wh-1 * 2*Ww-1, nH
# get pair-wise relative position index for each token inside the window
coords_h = torch.arange(self.window_size[0])
coords_w = torch.arange(self.window_size[1])
coords = torch.stack(torch.meshgrid([coords_h, coords_w])) # 2, Wh, Ww
coords_flatten = torch.flatten(coords, 1) # 2, Wh*Ww
relative_coords = coords_flatten[:, :, None] - coords_flatten[:, None, :] # 2, Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww
relative_coords = relative_coords.permute(1, 2, 0).contiguous() # Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww, 2
relative_coords[:, :, 0] += self.window_size[0] - 1 # shift to start from 0
relative_coords[:, :, 1] += self.window_size[1] - 1
relative_coords[:, :, 0] *= 2 * self.window_size[1] - 1
relative_position_index = relative_coords.sum(-1) # Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww
self.register_buffer("relative_position_index", relative_position_index)
self.qkv = nn.Linear(dim, dim * 3, bias=qkv_bias)
self.attn_drop = nn.Dropout(attn_drop)
self.proj = nn.Linear(dim, dim)
self.proj_drop = nn.Dropout(proj_drop)
nn.init.normal_(self.relative_position_bias_table, std=.02)
self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=-1)
def forward(self, x, mask=None):
B_, N, C = x.shape
qkv = self.qkv(x).reshape(B_, N, 3, self.num_heads, C // self.num_heads).permute(2, 0, 3, 1, 4)
q, k, v = qkv[0], qkv[1], qkv[2] # make torchscript happy (cannot use tensor as tuple)
q = q * self.scale
attn = (q @ k.transpose(-2, -1))
relative_position_bias = self.relative_position_bias_table[self.relative_position_index.view(-1)].view(
self.window_size[0] * self.window_size[1], self.window_size[0] * self.window_size[1], -1) # Wh*Ww,Wh*Ww,nH
relative_position_bias = relative_position_bias.permute(2, 0, 1).contiguous() # nH, Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww
attn = attn + relative_position_bias.unsqueeze(0)
if mask is not None:
nW = mask.shape[0]
attn = attn.view(B_ // nW, nW, self.num_heads, N, N) + mask.unsqueeze(1).unsqueeze(0)
attn = attn.view(-1, self.num_heads, N, N)
attn = self.softmax(attn)
else:
attn = self.softmax(attn)
attn = self.attn_drop(attn)
# print(attn.dtype, v.dtype)
try:
x = (attn @ v).transpose(1, 2).reshape(B_, N, C)
except:
#print(attn.dtype, v.dtype)
x = (attn.half() @ v).transpose(1, 2).reshape(B_, N, C)
x = self.proj(x)
x = self.proj_drop(x)
return x
class Mlp(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_features, hidden_features=None, out_features=None, act_layer=nn.SiLU, drop=0.):
super().__init__()
out_features = out_features or in_features
hidden_features = hidden_features or in_features
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(in_features, hidden_features)
self.act = act_layer()
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(hidden_features, out_features)
self.drop = nn.Dropout(drop)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.fc1(x)
x = self.act(x)
x = self.drop(x)
x = self.fc2(x)
x = self.drop(x)
return x
class SwinTransformerLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, num_heads, window_size=8, shift_size=0,
mlp_ratio=4., qkv_bias=True, qk_scale=None, drop=0., attn_drop=0., drop_path=0.,
act_layer=nn.SiLU, norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm):
super().__init__()
self.dim = dim
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.window_size = window_size
self.shift_size = shift_size
self.mlp_ratio = mlp_ratio
# if min(self.input_resolution) <= self.window_size:
# # if window size is larger than input resolution, we don't partition windows
# self.shift_size = 0
# self.window_size = min(self.input_resolution)
assert 0 <= self.shift_size < self.window_size, "shift_size must in 0-window_size"
self.norm1 = norm_layer(dim)
self.attn = WindowAttention(
dim, window_size=(self.window_size, self.window_size), num_heads=num_heads,
qkv_bias=qkv_bias, qk_scale=qk_scale, attn_drop=attn_drop, proj_drop=drop)
self.drop_path = DropPath(drop_path) if drop_path > 0. else nn.Identity()
self.norm2 = norm_layer(dim)
mlp_hidden_dim = int(dim * mlp_ratio)
self.mlp = Mlp(in_features=dim, hidden_features=mlp_hidden_dim, act_layer=act_layer, drop=drop)
def create_mask(self, H, W):
# calculate attention mask for SW-MSA
img_mask = torch.zeros((1, H, W, 1)) # 1 H W 1
h_slices = (slice(0, -self.window_size),
slice(-self.window_size, -self.shift_size),
slice(-self.shift_size, None))
w_slices = (slice(0, -self.window_size),
slice(-self.window_size, -self.shift_size),
slice(-self.shift_size, None))
cnt = 0
for h in h_slices:
for w in w_slices:
img_mask[:, h, w, :] = cnt
cnt += 1
mask_windows = window_partition(img_mask, self.window_size) # nW, window_size, window_size, 1
mask_windows = mask_windows.view(-1, self.window_size * self.window_size)
attn_mask = mask_windows.unsqueeze(1) - mask_windows.unsqueeze(2)
attn_mask = attn_mask.masked_fill(attn_mask != 0, float(-100.0)).masked_fill(attn_mask == 0, float(0.0))
return attn_mask
def forward(self, x):
# reshape x[b c h w] to x[b l c]
_, _, H_, W_ = x.shape
Padding = False
if min(H_, W_) < self.window_size or H_ % self.window_size!=0 or W_ % self.window_size!=0:
Padding = True
# print(f'img_size {min(H_, W_)} is less than (or not divided by) window_size {self.window_size}, Padding.')
pad_r = (self.window_size - W_ % self.window_size) % self.window_size
pad_b = (self.window_size - H_ % self.window_size) % self.window_size
x = F.pad(x, (0, pad_r, 0, pad_b))
# print('2', x.shape)
B, C, H, W = x.shape
L = H * W
x = x.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous().view(B, L, C) # b, L, c
# create mask from init to forward
if self.shift_size > 0:
attn_mask = self.create_mask(H, W).to(x.device)
else:
attn_mask = None
shortcut = x
x = self.norm1(x)
x = x.view(B, H, W, C)
# cyclic shift
if self.shift_size > 0:
shifted_x = torch.roll(x, shifts=(-self.shift_size, -self.shift_size), dims=(1, 2))
else:
shifted_x = x
# partition windows
x_windows = window_partition(shifted_x, self.window_size) # nW*B, window_size, window_size, C
x_windows = x_windows.view(-1, self.window_size * self.window_size, C) # nW*B, window_size*window_size, C
# W-MSA/SW-MSA
attn_windows = self.attn(x_windows, mask=attn_mask) # nW*B, window_size*window_size, C
# merge windows
attn_windows = attn_windows.view(-1, self.window_size, self.window_size, C)
shifted_x = window_reverse(attn_windows, self.window_size, H, W) # B H' W' C
# reverse cyclic shift
if self.shift_size > 0:
x = torch.roll(shifted_x, shifts=(self.shift_size, self.shift_size), dims=(1, 2))
else:
x = shifted_x
x = x.view(B, H * W, C)
# FFN
x = shortcut + self.drop_path(x)
x = x + self.drop_path(self.mlp(self.norm2(x)))
x = x.permute(0, 2, 1).contiguous().view(-1, C, H, W) # b c h w
if Padding:
x = x[:, :, :H_, :W_] # reverse padding
return x
class C3STR(C3):
# C3 module with SwinTransformerBlock()
def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, shortcut=True, g=1, e=0.5):
super().__init__(c1, c2, c2, n, shortcut, g, e)
c_ = int(c2 * e)
num_heads = c_ // 32
self.m = SwinTransformerBlock(c_, c_, num_heads, n)
2.2 yolo.py配置
不需要
2.3 yaml配置文件
增加以下yolov5_swin_transfomrer.yaml文件
代码
# YOLOv5 🚀 by Ultralytics, GPL-3.0 license
# Parameters
nc: 80 # number of classes
depth_multiple: 0.33 # model depth multiple
width_multiple: 0.50 # layer channel multiple
anchors:
- [10,13, 16,30, 33,23] # P3/8
- [30,61, 62,45, 59,119] # P4/16
- [116,90, 156,198, 373,326] # P5/32
# YOLOv5 v6.0 backbone by yoloair
backbone:
# [from, number, module, args]
[[-1, 1, Conv, [64, 6, 2, 2]], # 0-P1/2
[-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]], # 1-P2/4
[-1, 3, C3, [128]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]], # 3-P3/8
[-1, 6, C3, [256]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]], # 5-P4/16
[-1, 9, C3STR, [256]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]], # 7-P5/32
[-1, 3, C3STR, [512]], # 9 <--- ST2CSPB() Transformer module
[-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]], # 9
]
# YOLOv5 v6.0 head
head:
[[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 1, 1]],
[-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']],
[[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat backbone P4
[-1, 3, C3, [512, False]], # 13
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 1, 1]],
[-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']],
[[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat backbone P3
[-1, 3, C3, [256, False]], # 17 (P3/8-small)
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]],
[[-1, 14], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat head P4
[-1, 3, C3, [512, False]], # 20 (P4/16-medium)
[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]],
[[-1, 10], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat head P5
[-1, 3, C3, [1024, False]], # 23 (P5/32-large)
[[17, 20, 23], 1, Detect, [nc, anchors]], # Detect(P3, P4, P5)
]
修改完成